

Every Sunday, every commoner and noble went to church to a service spoken in Latin (which they didn't understand) and a sermon read from a Bible written in Latin (which they did not understand). It was generally the largest building in town often built in the shape of a cross.Churches had stained glass windows and statues that told stories from the Bible to the commoners and nobles who, for the most part, could not read. Parish ChurchThe parish church was the center of every town. As communities grew, their members often donated money and labor to build new and larger churches. Most Europeans were baptized, married, and buried by the Catholic Church.They also hosted feasts, festivals, and other celebrations. After each topic, write the main idea or a question you have regarding the topic.ĭaily LifeThroughout Western Europe in Medieval times, each community was centered around a church, playing a powerful role in nearly everyones personal life.The church offered religious services, established orphanages, and helped care for the poor, sick, and elderly. Read the information regarding the Roman Catholic Church.2. Feudalism was necessary because it provided all Europeans with food, shelter, order, structure, government, and economy. Commoners worked the nobles land in exchange for protections, food and shelter.3. Lords in turn provided land to lesser nobles, called vassals in exchange for loyalty and services.
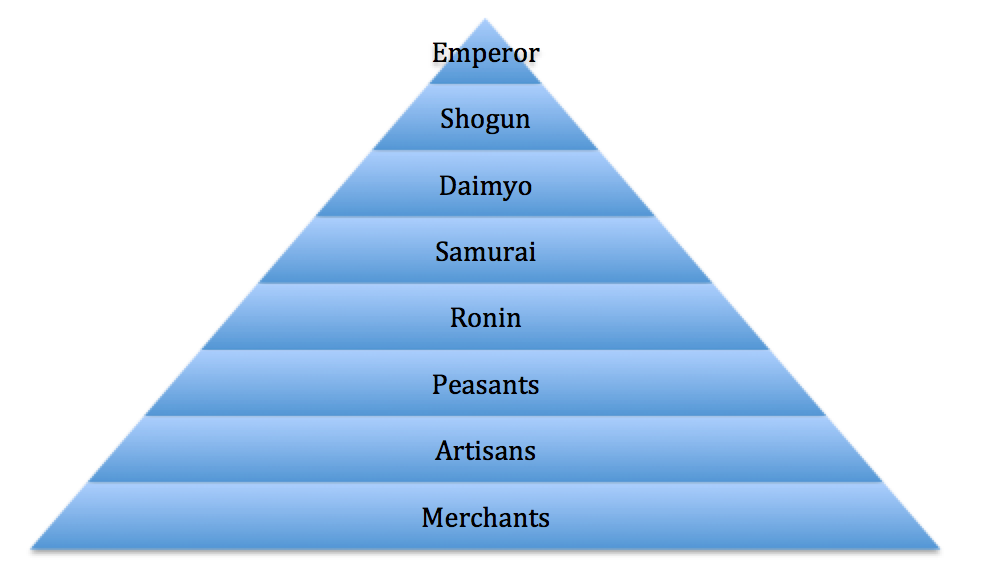
Kings gave land to powerful lords in exchange for loyalty. kingLordVassalKnight Nobles all aboveCommoners all belowPeasants, serfs, merchants, craftsmen2. Considered a local warlord Daimyo gives power to Samurai so that they will fight for him.Feudalism Quiz1. Shogun gives power to Daimyo in exchange for loyalty. Gives power to Shogun Shogun - Pledges loyalty to Emperor in return for power. The enemy were the Muslims who also wanted control of Jerusalem When Christians were successful, they tended to kill/mistreat the Muslims When the Muslims were successful, they tended to be tolerant of all faiths.Įmperor – King but more of a Figurehead Shogun – Military Warlords – Generals Daimyo – Landlords/landowners Samurai – Warrior class who provided various roles in Japanese government Seppuku – Ritual suicide in Japan Bushido – Code of Conduct for the SamuraiĮmperor Shogun Daimyo Samurais Artisans/ Peasants Emperor - Figure Head. A squire would take care of the Knight's horse, armor, and weapons When ready, the Squire would accompany the Knight into battle.ĩ Crusades European Knights would travel to the Middle East on Crusade The goal was to gain control of the city of Jerusalem. Steps to Knighthood: A boy must belong to a noble class At age 7 the boy would serve as a Knight’s page Learn knightly manners and how to care for weapons As a teenager the boy becomes a squire. This refers that peasants were responsible for all food production.Ĩ Becoming a Knight Knight – A mounted soldier who lived by the code of Chivalry and served a Feudal superior. Peasants were seen as “the backbone of Feudalism in Europe”. Receives land to work to grow food, and protection form Vassal. Receives land which he can then divide Peasants/Serfs – Gives labor, services, and product. Receive services, food, an army for protection and expanding land Vassal – Gives loyalty and fights for Noble. Vassals then own service to the Noble Chivalry – A European code of conduct that focusing on courage, loyalty, courtesy, and fighting fairly.ħ Benefits of Feudalism Noble – Give land. Nobles- Hereditary landowner of a privileged class in Europe Nobles would grant land (fief) to lesser nobles known as vassals. Medieval – The time period in the Middle Ages. Peasant s/Serfs Peasant s/Serfs Peasant s/Serfs Peasant s/Serfs Peasants /Serfs Peasants /Serfs Serfs would give a share of their produce to the Knights above them Knights would divide their land further and allow Serfs to work their land. King/Queen (Monarch) Lords/Nobles (Landowners) Knights The king gave land to Nobles The Nobles were loyal to the King Nobles would divide their land for knights Knights would defend the Nobles and act as an army.

The chart on European Feudalism demonstrates this. However, both Nobles and peasants received things they needed. The Feudal System was a system of social order after the fall of the Roman Empire In the Feudal system, the relationship between nobles and peasants were not equal. King/Queen (Monarch) Lords/Nobles (Landowners) Knights Peasant s/Serfs Peasants /Serfs Title: _ Role: _ Loyal to: Himself Lord/Noble Grant land to lesser nobles Title: _ Role: Allowed to live off, but not own fiefs Loyal to: _ Knights (Vassel)/ Lesser Nobles Lord/Noble Title: Peasant/Serf Role: _ Loyal to: _ Work the land for living and for prophet for their noble. 2 Feudalism – Chapter 13 worksheet Answers GRS


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
